Polymer additives for PMMA optimisation

How Polymeric Additives Are Revolutionizing PMMA Processing
Rising demands for resource efficiency, energy savings, and stable, high-performance manufacturing mean that even established materials like PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate) must reach new levels of performance. Plastics processors are looking for greater design freedom, improved flow behavior, shorter cycle times, and stable material properties—while also meeting regulatory and environmental requirements.
A recent collaboration between Polytives and Röhm demonstrates the enormous potential of modern Polymer additives for PMMA optimisation. By using the polymeric processing aid bFI A 3745, PMMA compounds can be specifically optimized—without compromising optical or mechanical properties.
Challenges in PMMA Processing and Why Additives Matter
PMMA is a well-established technical material, but new product generations demand:
- more filigree component geometries
- higher flowability
- lower processing temperatures
- reduced cycle times
- stable optical performance
The solution lies in fine-tuning the material—without changing the chemical structure of the base polymer. This is exactly where the Polytives additive comes into play.
The Polytives Additive: Hyperbranched PMMA for Superior Processability
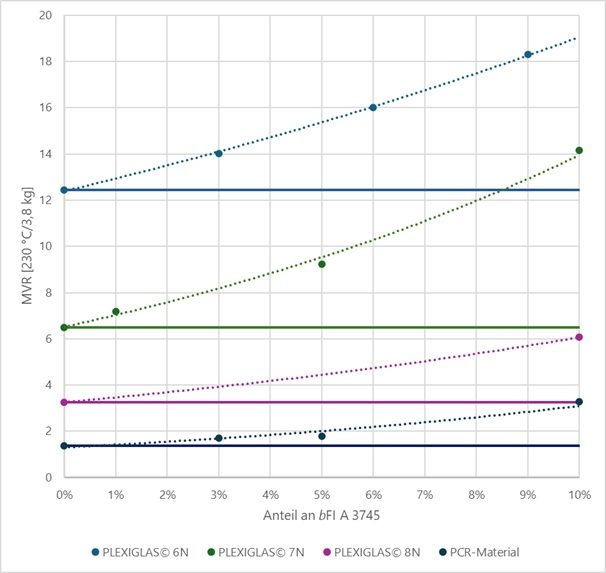
The additive bFI A 3745 consists of hyperbranched PMMA whose molecular architecture significantly improves melt dynamics.
Key advantages include:
- reduction of melt viscosity
- improved flowability
- lower processing pressures and temperatures
- gentler, more energy-efficient processing
- no migration thanks to polymeric structure
- full optical transparency remains intact
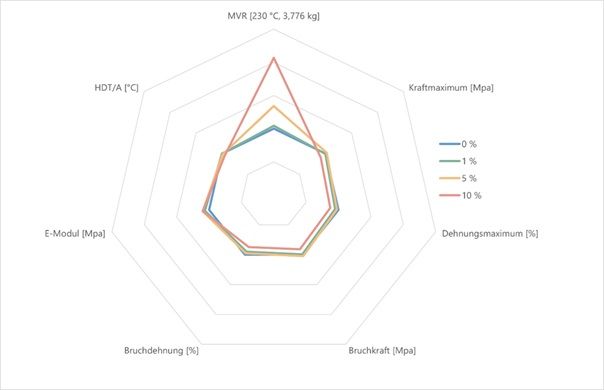
The effect becomes apparent at low dosage levels— even at 10% additive content, mechanical properties remain strong.
Measurable Improvements in Industrial Processing
Project data clearly shows how significantly PMMA compounds can be improved:
- temperature reduction of 10°C to over 35°C
- pressure reduction of up to 50%
- cycle time reduction of more than 20%
- MVR increase up to 100% (doubling)
For applications with strong cost and energy constraints—such as injection molding or compounding—this delivers an immediate competitive advantage.
No Compromises in Optical Quality or Long-Term Stability
Optical quality is essential in many PMMA applications. Testing confirms:
- no impact on transmission (200–800 nm)
- no significant yellowing (YI < 5)
- 10,000-hour weathering stability with no optical degradation
This makes the additive suitable for applications requiring high transparency and UV stability.
Why Modified PMMA Compounds Make a Difference
With the help of polymeric additives, existing materials can be improved without introducing completely new material systems. The benefits include:
- fast integration into existing production lines
- lower transition risks
- improved performance without design limitations
- more economical processes through shorter cycles and reduced energy consumption
This technology provides plastics processors with new opportunities to produce high-quality PMMA components more efficiently and more sustainably.
Conclusion: Polymeric Additives Are the Key to Energy-Efficient PMMA Processing
The project clearly demonstrates the potential of purpose-designed polymer additives. With bFI A 3745, PMMA compounds can be modified to enhance both processing performance and sustainability—without sacrificing optical clarity or mechanical strength.
For companies looking to modernize their production processes, polymer-based additives offer a future-ready and economically attractive solution. Learn more about Polymer additives for PMMA optimisation:








Recent Comments